Foundations of Adaptive Data Analysis
Classical tools for rigorously analyzing data make the assumption that the analysis is static: the models to be fit, and the hypotheses to be tested are fixed independently of the data, and preliminary analysis of the data does not feed back into the data gathering procedure. On the other hand, modern data analysis is highly adaptive. Large parts of modern machine learning perform model selection as a function of the data by iteratively tuning hyper-parameters, and exploratory data analysis is conducted to suggest hypotheses, which are then validated on the same data sets used to discover them. This kind of adaptivity is often referred to as p-hacking, and blamed in part for the surprising prevalence of non-reproducible science in some empirical fields.
 This project aims to develop rigorous tools and methodologies to perform statistically valid data analysis in the adaptive setting, drawing on techniques from statistics, information theory, differential privacy, and stable algorithm design. The technical goals of this project include coming up with information theoretic measures that characterize the degree to which a worst-case data analyst can overfit, given an interaction with a dataset, models for data analysts that move beyond the worst-case setting, and empirical investigations that bridge the gap between theory and practice. The problem of adaptive data analysis (also called post selection inference, or selective inference) has attracted attention in both computer science and statistics over the past several years, but from relatively disjoint communities. Part of the aim of this project is to integrate these two lines of work. The PI team spans departments of computer science, statistics, and biomedical data science. In addition to attempting to unify these two area, the broader impacts of this research will be to make science more reliable, and reduce the prevalence of “overfitting” and “false discovery”. The project also has a significant outreach and education component, and will educate graduate students, organize workshops, and produce expository materials.
This project aims to develop rigorous tools and methodologies to perform statistically valid data analysis in the adaptive setting, drawing on techniques from statistics, information theory, differential privacy, and stable algorithm design. The technical goals of this project include coming up with information theoretic measures that characterize the degree to which a worst-case data analyst can overfit, given an interaction with a dataset, models for data analysts that move beyond the worst-case setting, and empirical investigations that bridge the gap between theory and practice. The problem of adaptive data analysis (also called post selection inference, or selective inference) has attracted attention in both computer science and statistics over the past several years, but from relatively disjoint communities. Part of the aim of this project is to integrate these two lines of work. The PI team spans departments of computer science, statistics, and biomedical data science. In addition to attempting to unify these two area, the broader impacts of this research will be to make science more reliable, and reduce the prevalence of “overfitting” and “false discovery”. The project also has a significant outreach and education component, and will educate graduate students, organize workshops, and produce expository materials.
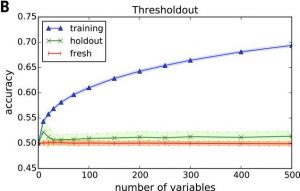
See our Science paper and the Penn News feature.
Collaborators
-
- Aaron Roth (CIS)
- Weijie Su (Wharton Statistics)
- Cynthia Dwork (Harvard Computer Science)
- Adam Smith (BU Computer Science)
- James Zou (Stanford Biomedical Data Science)
Funding
NSF, Sloan Foundation